Supervised Machine Learning Playground
This project uses a tree based model trained on weather data to predict rain, with a Streamlit application providing an interactive interface for users to fit the hyperparams and grid search.
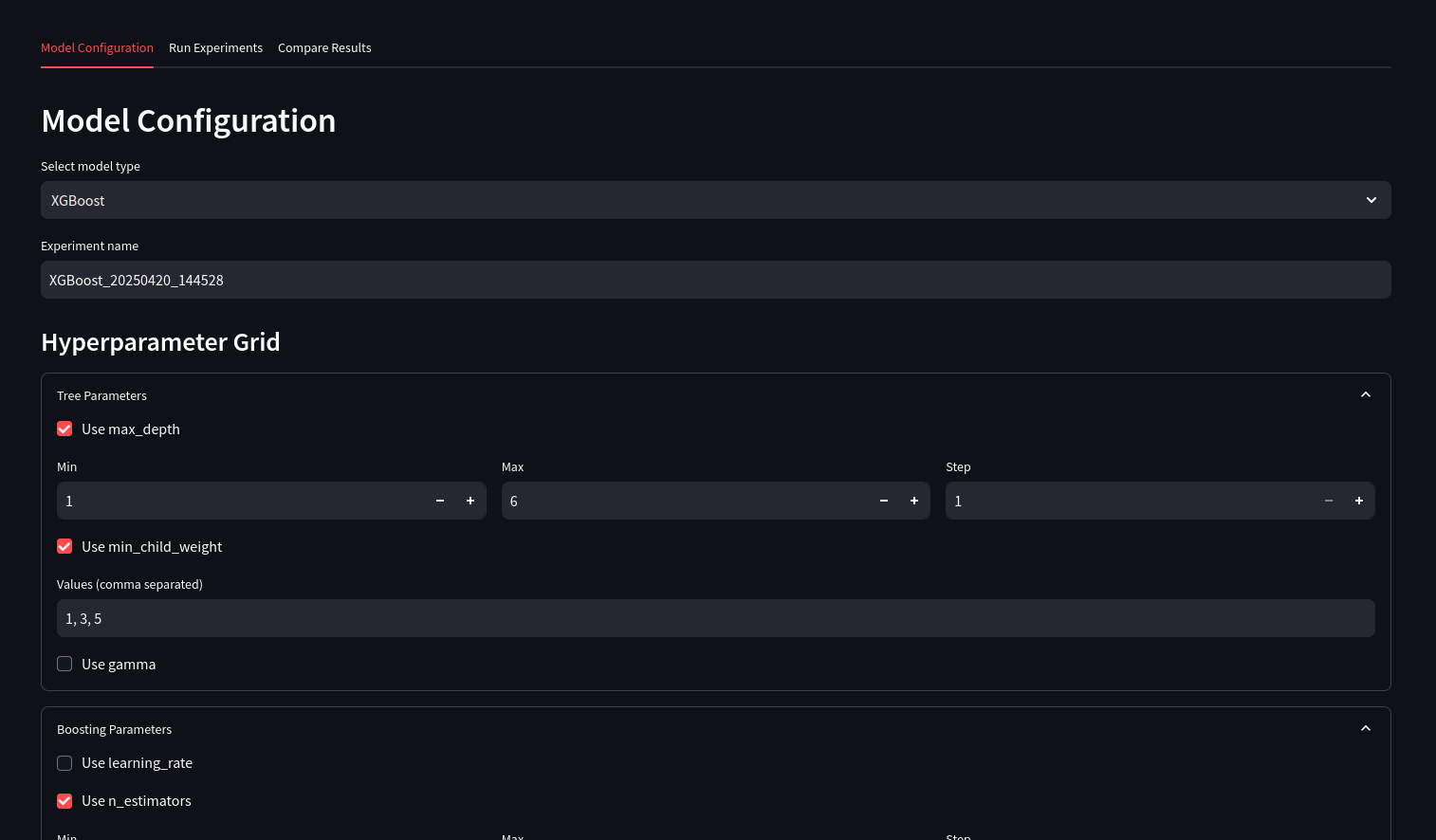
Project Prupose
This project is a supervised machine learning project focused on time-series forecasting, specifically predicting energy consumption (Usage_kWh) likely within the steel industry, based on temporal features. The project utilizes an XGBoost model, incorporates robust time-series cross-validation, and employs hyperparameter tuning to optimize performance. While the initial description mentioned weather data and rain prediction, the Streamlit script focuses on energy usage forecasting using time-based features derived from the “Steel_industry_data.csv” dataset.
Importance and Relevance
This project exemplifies a common and valuable workflow in data science, particularly in time-series analysis and forecasting. Here’s a breakdown of its key components and their significance:
-
Problem Framing:
- The goal is to predict future energy consumption (
Usage_kWh) based on historical data and time-related features (like time of day, day of week, month). This is framed as a supervised regression problem. - Relevance: Accurate energy consumption forecasting is crucial for resource management, cost optimization, grid stability, and anomaly detection in industrial settings.
- The goal is to predict future energy consumption (
-
Data Preprocessing:
- Temporal Feature Engineering: The script intelligently handles the ‘date’ column. Instead of using raw timestamps, it employs cyclical encoding (
cyclical_encodefunction) for features like hour, minute, day, and month. This represents the cyclical nature of time (e.g., hour 23 is close to hour 0) effectively for models. - Categorical Feature Handling: Features like ‘WeekStatus’ and ‘Day_of_week’ are converted into a numerical format using one-hot encoding (
pd.get_dummies). This is essential for most machine learning algorithms, including XGBoost, to process categorical data. - Relevance: Proper preprocessing is critical. Cyclical encoding captures temporal patterns accurately, while one-hot encoding allows the model to learn from categorical distinctions without imposing ordinal relationships.
- Temporal Feature Engineering: The script intelligently handles the ‘date’ column. Instead of using raw timestamps, it employs cyclical encoding (
-
Time-Series Data Splitting:
- The data is split chronologically into a training/validation set and a held-out test set (last 20% of data).
- Crucially, within the training/validation phase,
TimeSeriesSplitfromsklearnis used for cross-validation. - Relevance: This approach is vital for time-series data. Standard k-fold cross-validation would shuffle data, leading to data leakage (training on future data to predict the past), resulting in overly optimistic performance estimates.
TimeSeriesSplitensures that validation folds always occur after training folds, mimicking a real-world forecasting scenario.
-
Model Selection (XGBoost):
- The project uses
XGBRegressor, an implementation of gradient boosted trees. - Relevance: XGBoost is a powerful and widely-used algorithm known for its performance, efficiency, and ability to handle complex, non-linear relationships in tabular data. It incorporates regularization techniques to prevent overfitting and often yields state-of-the-art results in regression and classification tasks. Its ability to handle different feature types makes it suitable here.
- The project uses
-
Hyperparameter Tuning:
GridSearchCVis employed to systematically search through a predefined grid of hyperparameters (n_estimators,max_depth,learning_rate,subsample). It uses theTimeSeriesSplitstrategy and (scoring="r2") as the evaluation metric to find the best model configuration.- Relevance: Tuning hyperparameters is essential for optimizing model performance.
GridSearchCVprovides a structured way to explore the hyperparameter space, ensuring the chosen model is well-suited to the specific dataset and problem, validated through appropriate cross-validation.
-
Evaluation and Persistence:
- The best model found via
GridSearchCVis evaluated on the held-out test set. This provides an unbiased estimate of the model’s generalization performance on unseen data. Regression metrics are calculated using a customRegressionMetricsclass. - The trained model is saved (using a custom
Storageclass) for potential later use, preventing the need for retraining. - Relevance: Evaluating on unseen data is the gold standard for assessing model viability. Saving the model (
XGBoost.pickle) is a key step towards deploying the model, perhaps in the interactive Streamlit application mentioned in the initial description, allowing users to interact with the predictions or explore parameters without rerunning the entire training pipeline.
- The best model found via
Summary
This project could be a improvement for tackling time-series forecasting problems using modern data science tools and techniques. It highlights the importance of careful preprocessing tailored to temporal data, the necessity of appropriate cross-validation strategies like TimeSeriesSplit, the power of models like XGBoost, and the critical role of hyperparameter tuning and final evaluation on unseen data. The workflow implemented in pipeline.py represents a practical and effective approach applicable to many real-world forecasting challenges. The potential integration with an interactive tool like Streamlit would further enhance its utility for exploration and demonstration.